Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Notes PDF
In thi post we are providing notes Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1. The PDF download link is given at the bottom.
The PDF Download link is given at the bottom.
Birth of agriculture
Till 10,000 B.C.E. people were nomadic. This means that they were wandering in groups from place to place in search of food and shelter. Later, agriculture was born.
Crop
When plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. The crops can be classified on the basis of the season in which they grow. In India, crops can be broadly categorised into two types given in the following table.
Type of crop | Growing season | Examples |
Rabi crops | Rainy season (Generally from June to September) | Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut and Cotton |
Kharif crops | Winter season (October to March) | Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed |
Basic agricultural practices/basic steps of crop production
The process of crop production involves a number of steps like selection of seeds, sowing, etc.
(1) Preparation of soil
It is necessary to prepare soil by tilling through ploughs and by levelling through levelers. Tilling or ploughing is the process of loosening and turning of the soil. Tilling has following benefits.
- Ensures deep penetration of roots into the soil.
- Helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil and called friends of farmers since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
- Brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top
The ploughed field may have big clumps of soil called crumbs. Before sowing the seeds, it is necessary to break soil clumps through plough, hoe and cultivator to get better yield
(2) Sowing
Sowing of seeds at appropriate depths and distances gives good yield. Good varieties of seeds are sown after selection of healthy seeds. Sowing is done by seed drills. While sowing, appropriate distance between the seeds avoids overcrowding of plants and allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water from the soil.
(3) Adding manure and fertilisers
Soil needs replenishment and enrichment through the use of organic manure and fertilisers.
- Manure: Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Manure is considered better than fertilisers. Its advantages are given below.
Advantages of manure:
- Manure enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- Manure makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
- Manure increases the number of friendly microbes.
- Manure improves the texture of the soil.
- Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil
- Fertilisers: Fertilisers are chemicals which are rich in a particular nutrient. Some examples of fertilisers are— urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium). Fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. Use of chemical fertilisers has increased tremendously with the introduction of new crop varieties.
- Crop rotation: It is another method of replenishing the soil with nutrients. In crop rotation, different crops are grown alternately.
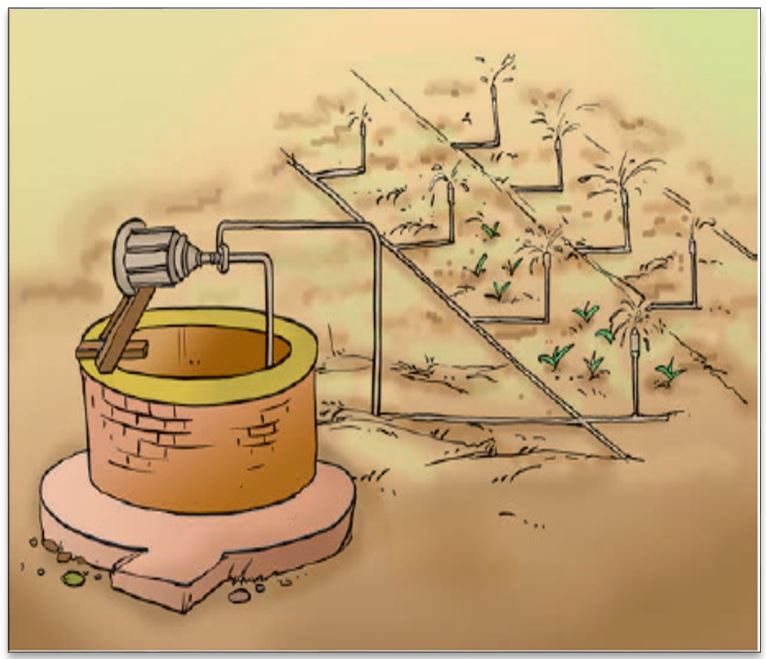
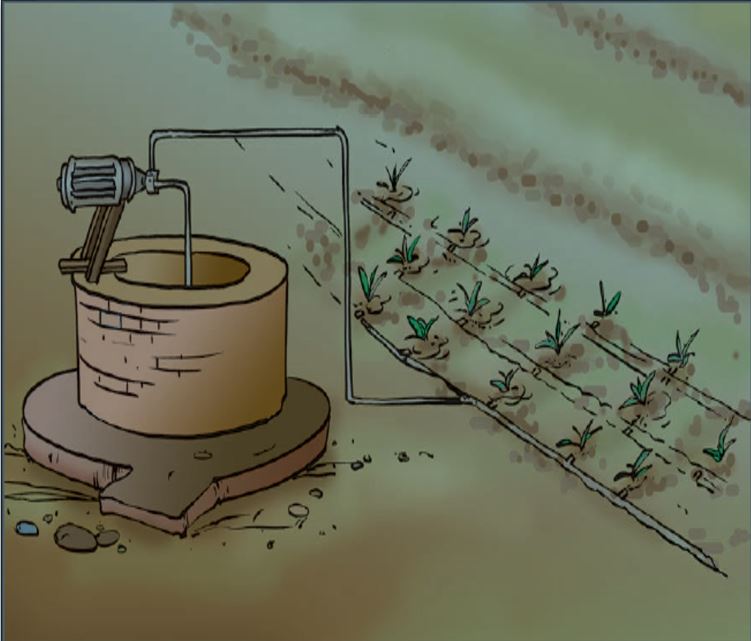
(4) Irrigation
Supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called irrigation. Wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals are sources of irrigation for water. Moat (pulley-system), chain pump, dhekli and rahat (Lever system) are traditional methods (ways) of irrigation. Sprinkler system and drip system are modern methods of irrigation. Following table provides a brief comparison of these modern methods of irrigation.
Difference between Drip Irrigation and Sprinkler irrigation
Sprinkler system | Drip system
|
It is more useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available. | It is a boon in regions where the availability of water is poor. Water is not wasted at all. |
In this system, water gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. | In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. |
Sprinkler system is very useful for lawns, coffee plantation and several other crops. | It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. |
(5) Protecting from weeds
Weeding involves the removal of unwanted and uncultivated plants called weeds. Weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space, and light and affect the growth of the crop. Weeds are removed manually with the help of Khurpi or controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2, 4-D. Tilling also helps in control of weeds.
(6) Harvesting
Harvesting is the cutting of the mature crop manually or by machines. Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing. Farmers with small holdings of land do the separation of grain and chaff by winnowing. Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu are special festivals associated with the harvest season.
(7) Storage
Proper storage of grains is necessary to protect them from pests and microorganisms. Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home.
Animal husbandry: Food is also obtained from animals for which animals are reared. This is called animal husbandry.

.png)



0 Comments